Dose titration at home during covid 19
Achieving target glycaemic control is essential in people with diabetes to minimize the risk of long-term complications.
Basal insulin allows a simple and safe dose titration
Important steps to follow
-
 STEP 1
STEP 1
Record your fasting blood glucose
-
 STEP 2
STEP 2
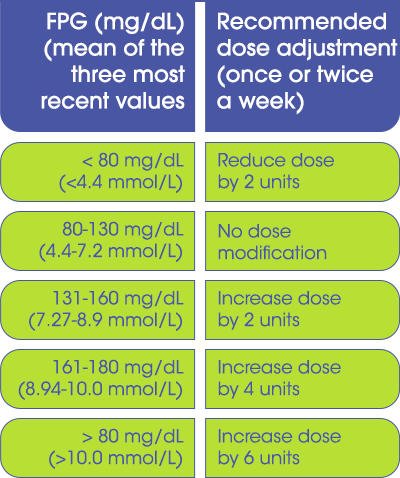
Check the reading and dose in the table below
-
 STEP 3
STEP 3
Adjust your Basal insulin dose by adding the recommended units to your existing Basal insulin dose
-
FPG (mg/dL) (mean of the three most recent values
-
Recommended dose adjustment (once or twice a week)
-
< 80 mg/dL (4.4 mmol/L)
-
Reduce dose by 2 units
-
80-130 mg/dL (4.4-7.2 mmol/L)
-
No dose modification
-
131-160 mg/dL (7.27-8.9 mmol/L)
-
Increase dose by 2 units
-
161-180 mg/dL (8.94-10.0 mmol/L)
-
Increase dose by 4 units
-
> 80 mg/dL (>10.0 mmol/L)
-
Increase dose by 6 units
Example:
Current Basal Insulin dose: 18 U | Current fasting glucose: 155 mg/dL
New Basal insulin dose: 18+2 = 20 U
Consult your doctor for any queries
References:
Bajaj, S., Das, A.K., Kalra, S. et al. BE-SMART (Basal Early Strategies to Maximize HbA1c Reduction with Oral
Therapy): Expert Opinion. Diabetes Ther 10,
1189-1204 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-019-0629-z.
FPG: Fasting Plasma Glucose.
BE-SMART - Basal Early Strategies to Maximize HbA1c Reduction with Oral Therapy.